
Health Institutions
Description
Nuclear Medicine is new modality in Imaging .
 This is special from other type of Imaging modality (e.g. CT, MRI), using the radioactivity
in the form of liquid, capsule and gases for diagnostic imaging procedures. The
most widely used radioactivity in Nuclear Medicine is Tc99m (Technetium) which in
liquid form, more optimum energy level (140Kev) for imaging, pure gamma emitter.
In SMC Nuclear Medicine Department we do all type of imaging procedures including
some therapeutic procedures like I131 treatment for Graves Diseases.
This is special from other type of Imaging modality (e.g. CT, MRI), using the radioactivity
in the form of liquid, capsule and gases for diagnostic imaging procedures. The
most widely used radioactivity in Nuclear Medicine is Tc99m (Technetium) which in
liquid form, more optimum energy level (140Kev) for imaging, pure gamma emitter.
In SMC Nuclear Medicine Department we do all type of imaging procedures including
some therapeutic procedures like I131 treatment for Graves Diseases.
By selecting a radiopharmaceutical with appropriate properties, a range of organs and functions can be examined. Technetium-99m (99mTc) is used for most examinations. It produces only gamma rays - no harmful alpha or beta particles. it has a half-life of 6 hours, allowing time for the image acquisition but decaying to negligible levels in a day or two. It is readily obtainable from a portable molybdenum generator and, being a transitional element, can be easily bound to a range of organic compounds with appropriate pharmacological properties. 99mTc-labelled hepatoiminodiacetic acid (99mTc/HIDA) is useful in hepatobiliary imaging as its secretion is similar to that of bile. For perfusion lung scanning, the isotope 99mTc-lablelled macroaggregated albumin is used. The small particles labeled with the isotope demonstrate pulmonary blood flow.
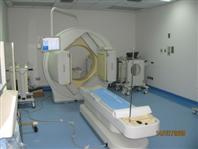
Nuclear Medicine Section and Equipment
The unit has one sate-of-art radionuclide imaging system and one new hot lab room. One is a single head SPECT camera manufactured by Siemens (Diacom). The 2nd is a Dual head SPECT camera manufactured by philips. Both systems are connected to a hard copy printer (Dry star printer Agfa 2000 color) which is connected to a high resolution color printer (paper).
The dual head gamma is mostly used for lot of procedures. Because it rotates in elliptical path rather than orbital path. When it rotates on elliptical path the distance between the patient and camera is less so the resolution will be improved. We do SPECT, whole body and planner imaging.
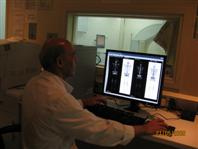
The radiopharmaceutical is prepared in hot lab. It is located just away from department we do all type of labeling. All radiopharmaceutical is prepared in hot lab in morning at 7a.m. (e.g. TC – HDP, DTPA, etc) The radioactivity will be ready at 8:00a.m. for injection. Before injection we have to calculate the correct dose to the patient according to the weight of the patient. In hot lab we are preparing isotopes from Generators (Mo 99 – generators). This process is called eluting. First elute (Tc 99m) Technetium from Generator and the labeling with desired cold kits (e.g. MDP, DTPA, etc…) injecting to the patient. The quality control of labeling efficiency should be done before injection. It should be above 95%.
Type of Imaging and Studies
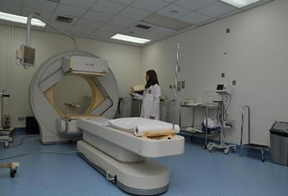
There are different type of Imaging in Nuclear Medicine. Like static scanning dynamic
scanning, planar and SPECT acquisition. Whole body scanning also done to all type
of bone scans. Depending on the energy level of isotope, we have to change the protocol
and collimeters. SPECT acquisition for the cardiac patient is normally done more.
We do all type of internal organ studies. (e.g. bone, renal, liver, etc…) cardiac
perfusion studies are most widely done here. Lung perfusion scan and G.I. bleeding
scan are done on emergency basis. 24 hours one technologist will be covering the
on call duties. I131 therapy also be given to the patient for Graves Disease.
Procedure
Most of the NM procedures do not require any preparation. Some studies require preparation such as:
- Cardiac study, I131/ survey and pediatric studies like HIDA & Meckel's scan.
- Usually patients have to stop B- Blockers for cardiac studies and Eltroxin for I¹³¹ survey studies. Patients have to take some medicine to enhance the image quality in pediatric studies.
- In general, patients are injected with a small volume of radioactive tracer. In some procedures (eg. Thyroid scanning), radioactive capsules are administered orally.
- Patients always lie in the supine position on the scanning table. The detector rotates around the patient at 360° or 180°, alternatively the scanning table moves.
-
The patient is positioned by the Technologist according to the study. The patient
is advised not to move during the study.
Precautions
- The diagnostic radioactive tracer does not have any side effects.
- The patient has to take extra water after the examination to reduce the radiation dose to him /her self .
- Generally radioactive tracers should not be administered during pregnancy. Female patients must make sure that they are not pregnant.
- During lactation breast feeding must be withdrawn for 24 hours ( TC -Scans) .
Precaution During The Radioactivity Administration

- Every female patient below 60 should be ruled out for pregnancy.
- If they are breast feeding they should stop feeding for 24 hours (Tc) and 30 days for I131.
- All radioactivity should administered in a proper lead shielding.
- No spillage of radioactivity is allowed in the department proper instruction should be given to the injected patient.
Location and contact
The Nuclear Medicine rooms are located in ground floor SMC -Radiology Department.
Ext. No. 4017/4035 Dir. 17284017 / 17284035
Available Staff
Two Consultant Nuclear Medicine Physician:
Dr. Abdulhameed Alawadhi / U.J. Nabar Consultant Radiologist
Head of NM is Mr. Nader Mohd Ali
Two Radiologic Technologists:
Mr. Yesudass Jaipaul & Mr. Manivannan K.
One Senior Radiography Technician:
Mr. Moh'd Jaffer.
Two Nuclear Medicine Physicists:
Mr. Jagadeesh Babu and Mrs. Nada Ali Ahmed
One Staff Nurse:
Mrs. Widad Jaffer Moh'd.
Timing
Sundays to Thursdays from 7:00 AM to 3:00 PM
+24 hours round the clock one radiologist and technologist on call duty.


