
Computed Tomography Scanner (CT Scan)
Description
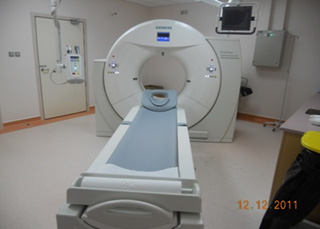
CT or sometimes called Computerized Axial Tomography Scanner (CATS), uses special X-Ray equipment to obtain many images from different angles, and then join them together to show a cross-section of body tissues and organs. CT scanning provides more detailed information than do plain radiographs. It also can show bone, soft tissues, and blood vessels in the same CT images.
In CT, the X-Ray tube is rotated around the patient and the X-Ray beam impinges
on an array of detectors as it emerges from the patient. The intensity of the transmitted
beam at each angle is recorded.
By a computer technique involving the solution of many simultaneous equations, a
two-dimensional image is produced of an axial slice through the patient. The value
of each pixel depends on the attenuation of the X-Ray beam by the small volume of
the tissue that the pixel represents. As with conventional radiography, there is
differential attenuation of the beam by tissues of different atomic weight and density.
 With CT, very small differences in attenuation can be detected, allowing differentiation
of soft tissue compositions. The Hounsfield scale is used, by convention, as a measure
of radiation attenuation of tissue in CT. Water has a value of zero; soft tissues
are usually in the range 20 to 60, whereas calcium is over 100, fat is in the range
-40 to -80, and air is -1000. The advent of CT revolutionized diagnostic imaging
of the central nervous system by allowing noninvasive imaging of intracranial structures.
It has subsequently found many further application, especially in the mediastinum
and retroperitoneum.
With CT, very small differences in attenuation can be detected, allowing differentiation
of soft tissue compositions. The Hounsfield scale is used, by convention, as a measure
of radiation attenuation of tissue in CT. Water has a value of zero; soft tissues
are usually in the range 20 to 60, whereas calcium is over 100, fat is in the range
-40 to -80, and air is -1000. The advent of CT revolutionized diagnostic imaging
of the central nervous system by allowing noninvasive imaging of intracranial structures.
It has subsequently found many further application, especially in the mediastinum
and retroperitoneum.
The first CT scan in Bahrain was installed in SMC on 1st August 1985 and was manufactured
by GE.
Procedure
No special preparation is needed for a CT scan of the head unless the patient has to receive a contrast material - a substance that highlights the brain and its blood vessels and makes abnormalities easier to see.
Precautions
CT does involve exposure to radiation in the form of X-Rays, but the benefit of
an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk. Special care is taken during X-Ray
examinations to ensure maximum safety for the patient by shielding the abdomen and
pelvis with a lead apron, with the exception of those examinations in which the
abdomen and pelvis are being imaged. The effective radiation dose from a NC CT brain
is about 2 mSv which is about 1 year's exposure from background radiation or equivalent
to 100 chest X-Rays.
Women should always inform their doctor or X-Ray technologist if there is any possibility
that they are pregnant. Scanning is NOT allowed for pregnant women. In some cases
an alternative study will be performed to reduce or eliminate the radiation exposure
to the fetus. Contrast materials contain iodine, which can cause a reaction in persons
who are allergic. The radiologist also should know if the patient has asthma or
any disorder of the heart or renal function.
Benefits
-
CT examinations are relatively fast and of a reasonable cost especially when compared
to MRI.
-
The best imaging modality that provides detailed images of bone and calcification.
-
CT is becoming the method of choice for rapidly screening trauma victims to detect
internal bleeding or other life threatening conditions.
-
Life support equipment can generally be easily used in the CT room; unlike MRI.
-
Pulmo CT: lung scanning triggered by pat. breathing, with evaluation of lung tissue
CT values.
-
Post processing, image evaluation & annotation, labeling, image rotating, measurements,
magnification and reconstruction from axial images to 3D image, sagittal, oblique,
coronal, etc.
-
System components: the gantry system (the heart of the whole system - tilted 30
degree -/+), the operating console, the optical drive MOD magneto-optical disc for
data storage & keyboard. Computer software and laser imager.
-
Topogram frontal or lateral survey scan, similar to a conventional X-Ray exposure.
Location and Contact
Radiology has two CT Scans systems, both they are located in the new SMC building ground floor.
CT Scan No.1 Tel. No. Ext. 4014 Dir. 17284014 / 17284035
CT Scan No. 2 Tel. No. : Ext. 4010 Dir. 17284010
CT appointment office Ext. No: 4005 , Tel. No.: 17284005
Equipment
SMC has three C.T. Scan systems, two units are manufactured by Siemens one is Sensation16
and 2nd is 128 Definition AS - MDCT) those two are belong to the Radiology Department
and the 3rd unit for Oncology Department and it is manufactured by Philips (it is
16 Slices CT).
N.B.The first CT scan in Bahrain was installed in SMC on 1st August 1985 and was
manufactured by GE.
Available Staff
Consultant Radiologist and sometimes one chief or senior resident radiologist as per the duty rota.
The CT inc-charge: Mrs. Afaf AlAradi
The Senior Radiographers: Mr. Hussain AlFardan/ Abbas Mahdi/ Rashid Al.Aradi/ Muneer Ma'aroof/ Mooza Mubarak/ Amira Hassan
Radiographers: Hussain Al.Awami / Sayed Mohd/ Nasser Ghuloom/ Abdulla Hassan/ Ahmed Jaffar/ Hasan Hilal/ Mrs.Kubra Isa.
For more information see the radiologists monthly rotation list.
Staff Nurse: Mrs. Kawkab Isa.
Timing
Sunday to Thursday from 7:00 AM to 2:00 PM
+24 hours Radiologists & Radiographer on-call


